History of taxonomic concepts
History of taxonomic concepts:
Linnaeus, 1735 – 2 Kingdoms – Animalia, Vegetabilia
Haeckel, 1866 – 3 Kingdoms – Protista, Plantae, Animalia. Image Haeckel's tree of life.
Chatton, 1937 – 2 Empires – Prokaryota, Eukaryota
Copeland, 1956 – 4 Kingdoms – Monera (prokaryotes), Protoctista, Plantae, Animalia
Whittaker, 1969 – Monera (prokaryotes), Fungi, Protista, Plantae, Animalia
Woese et al, 1977 – 6 Kingdom – Eubacteria, Archaea, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
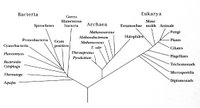
Woese and Fox, 1999 – 3 Domain system: Eubacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes.
Table Comparisons of Eubacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes - The Three Domains View Quicktime Movie - Genetic Data movie of phylogram construction - image cladogram - image Tree of Life— Lateral Gene Transfer Diagram - image uprooted tree - image 16S ribosomal RNA - image The "Shrub of Life" - image A comparison of key characteristics from the three domains of life - enlarged - image Whale phylogeny - Genomics Animations and Images - Proteins & Proteomics - Animations and Images – Evolution and Phylogenetics - Animations and Images - Human Evolution - Animations and Images - Genetics of Development - Animations and Images – Cell Biology & Cancer - Animations and Images - Neurobiology - Animations and Images - Biology of Sex & Gender - Animations and Images - Genetically modified organisms - Animations and Images - Biodiversity - Animations and Images – Microbial Diversity – Animations and Images – Emerging Infectious Diseases - Animations and Images – HIV & AIDS - Animations and Images :
Labels: Chatton, Copeland, Fox, Haeckel, history, Linnaeus, Whittaker, Woese