Taxonomy of the bacteria was historically based on phenotypical physical and chemical characteristics – phenetic taxonomy. According to "Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology", all bacteria can be classified into four divisions, or phyla according to the constituents of their cell walls.
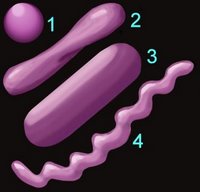 Each division was further subdivided into sections according to :
Each division was further subdivided into sections according to :
1. Reaction of the cell wall to the Gram stain due to thick layer of peptidoglycan (Gram +ve) or thin layer of peptidoglycan (Gram -ve). The cell walls of Archaeobacteria contain no peptidoglycan.
2. Shape (left) – cocci (1), pleomorphic (2), bacillus (3), helical (4)
3. Arrangement of cells
4. Oxygen requirement – aerobic, anaerobic, or facultative anaerobe
5. Motility – flagellated, non-motile
6. Specific nutritional requirements
7. Metabolic properties – autotrophic (chemical or photosynthetic), heterotrophic
The advent of genomics and examination of 16s ribosomal RNA has led to modifications in the classification of the prokaryotes, with the older nomenclatures revised into new classifications of Phyla. (diagram at bottom) Woese and Fox proposed the Three Domain system: Eubacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes. When Woese and Fox proposed the 3 Domain system, the term 'Urkaryotes' was proposed for ancestors of eukaryotes prior to their endosymbiotic acquisition of mitochondria and chloroplasts from prokaryotes.
"Misunderstanding the Bacteriological Code"
The Three Domain system is increasingly accepted. Free Full Text Article : Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdoms. Woese CR, Fox GE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088-90.
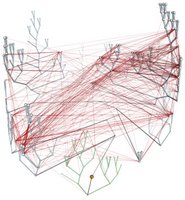 Left - click to enlarge image: Horizontal gene transfer - gene swapping - has blurred the evolutionary relationships (image) of prokaryotes, and continues to provide a mechanism for the sharing of antibiotic resistance between bacteria. See: Trees, vines and nets: Microbial evolution changes its face.
Left - click to enlarge image: Horizontal gene transfer - gene swapping - has blurred the evolutionary relationships (image) of prokaryotes, and continues to provide a mechanism for the sharing of antibiotic resistance between bacteria. See: Trees, vines and nets: Microbial evolution changes its face.
Phylogenetic separation into evolutionary relationships (clades), based on comparison of genomes is likely to supplant phenotypical (phenetic) taxonomies of the prokaryotes.(nomenclature)
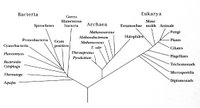
Right - click to enlarge image: Based on Woese's proposed scheme based on the 16s subunit of ribosomal RNA, which appears to better illustrate evolutionary relationships within the 3 domains.
Labels: 16s rRNA, 3 Domain, Archaeobacteria, bacteria, Eubacteria, Fox, gram, taxonomy, Woese













































